Deep Learning vs Machine Learning vs AI – What’s the difference?
If you are conversant with emerging trends, especially in the technological field, you are likely to have come across the terms, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning. To the layman, the terms are identical, and many even use them interchangeably. However, as a German computer expert, Andrew Bulezyuk, states the three terms are very different and are used in separate applications. Any expert in the field knows just as much.
So, what is the difference between deep learning, machine learning and artificial intelligence, and how do they relate to one another? The figure below should help you get a basis to begin with.
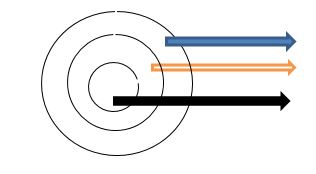

As you can see from the figure above, the three terms – artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning, are all part of the same concept. Artificial Intelligence is the main concept, followed by machine learning (ML), which is a subset of AI, and finally, deep learning – a subset of machine learning. Both deep learning and machine learning are techniques for achieving artificial intelligence. However, before we dig deeper into that, let’s first define the three terms in the simplest way possible.
What is Artificial intelligence (AI)?
Artificial intelligence, just like the name suggests, refers to the ability of a computer program to function like a human brain. There are many technologies that are incorporating AI systems today, and although we are yet to accomplish AI fully, there is hope that in the future, we will definitely hit the target.
However, the term AI is very general, especially since it is the original concept of developing systems that can behave and make logical decisions just like humans beings. AI, therefore, encompasses everything, from good old fashioned AI (GOFAI) to the more recent technologies like deep learning.
Every time a machine performs a task, based on a set of predetermined instructions that solve problems (algorithms), we refer to such “intelligent” behaviour as AI. For example, we can have machines that automatically recognize when a hand is raised up or other such automation.
There are two categories of artificial intelligence; general AI, like the example we have above, and narrow AI, which can do perform more intelligent jobs, sometimes even better than human beings. Social media platforms like Pinterest employ narrow intelligence technology to classify various images.
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine learning can be loosely translated to mean, enabling a machine to learn on its own. To better understand machine learning, think of the data mining concept. Data mining refers to the technique of analyzing a large stored database and deriving new information from the database. Machine learning employs the same technique, so we can say that machine learning is in some way, a data mining technique. Now you understand, right?
A simple way to define the concept would be; machine learning is a technique of analyzing data, learning from the data, and employing the knowledge to make an informed decision. Thus, a machine learning technique helps us achieve artificial intelligence.
By training algorithms to learn, ML intends to empower machines with the ability to learn from the provided data and make correct predictions. The training in machine learning, however, requires a lot of data input to the computer algorithms, to allow learning from the processed information.
Consider the table below:
| Weight (grams) | Texture | Fruit Type |
| 155 | Rough | Orange |
| 180 | Rough | Orange |
| 135 | Smooth | Apple |
| 110 | Smooth | Apple |
| 120 | Smooth | ? |
As you can see from the above table, the orange and apple fruits are being categorized based on weight and texture. However, the last row only has information on the fruit’s weight and texture, leaving the computer program to determine the type of fruit.
When the training data is fed into the computer algorithm, the system can learn the various characteristics of apples and oranges. Thus, when provided with only information on weight and texture, the machine can correctly predict the type of fruit in question. Such is the essence of machine learning.
Real-Life Applications of Machine Learning
Some of the mega-companies we have today are using machine learning technologies to give users a better experience. For example, Amazon uses machine learning to figure out the preferences of various customers to give better product choice recommendations. Netflix also uses machine learning technology to give various users suggestions on the movies and TV shows to watch.
What is Deep Learning (DL)?
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning. We can say that deep learning is a technique of realizing machine learning, or in simpler terms, deep learning is the next evolution after machine learning. Deep learning functions just like machine learning, only that the technique involved is more complicated. Therefore, DL has more advanced capabilities compared to machine learning.
Deep learning is inspired by the human brain’s information processing patterns. DL algorithms can, therefore, process information just like human brains. Basically, our brains find patterns and organize various types of information, thus, deciphering the new information received. DL algorithms can be trained to operate in a similar manner, enabling machines to process information and perform tasks like human beings.
When we receive new information, we are able to interpret the information because our brains compare the new information with the other items we know, thus, making sense of the new information. The same concept is applied by DL algorithms.
Deep learning employs several layers of algorithms to interpret data, thus, easily finding related patterns and making correct predictions. Several layers of algorithms are referred to as artificial neural networks (ANN). The name is from the inspiration of the neural networks present in human brains.
Udemy vs. Udacity: Detailed Comparison & Which One is Better?
Application of Deep Learning (DL) Algorithms
To better understand how deep learning works and the difference between machine learning, let us look at a simple application. Assume we have a flashlight and we train a machine learning system to turn on the light whenever someone says “dark”. The machine learning model will analyze the various phrases uttered by people in the room and look for the word “dark”. Whenever the utterance is made, the system will recognize the need for light and on the flashlight.
However, this approach may have a defect that cannot be solved by the machine learning system. Let us assume someone in the room says, “This room is so dim, I cannot see properly”. The logical thing in such a situation would be for the flashlight to be turned on, but since the sentence lacks the word “dark”, the system will not turn on the flashlight.
Now here we see the difference between deep learning and machine learning model. If a deep learning model was used in the scenario, the system would work automatically on the flashlight. Deep learning models can learn from their computing and accomplish more.
Deep Learning vs Machine Learning vs AI
The following are the major differences between machine learning and deep learning.
| Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
| Machine learning algorithms always require structured data to give the desired results. | DL algorithms rely on ANN (Artificial Neural Networks) to interpret data for the desired output. |
| ML algorithms are designed to “learn” by interpreting labelled data, and then use the information to give more outputs. However, sometimes the output is incorrect, and in such instances, the machine learning systems need to be retrained through human intervention. | Deep learning algorithms do not require human intervention. The nested layers in the neural networks pass the data through hierarchies of different concepts to come up with the correct interpretation. In case of any mistakes, the deep learning models will learn from the errors and make better predictions. |
| ML algorithms rely on labelled data, and as such, they are not preferable for complex queries involving large volumes of data. | Deep learning neural networks are most suitable for use on a large scale. DL algorithms are best suited for complex calculations rather than simple tasks. |
| ML algorithms do not require as much data compared to DL algorithms. The reason is that ML algorithms use pre-programmed criteria in learning and performing tasks. | DL algorithms require much more data because the systems are only identified by various concepts and differences when exposed to millions of data points. |
Why do many people associate deep learning and machine learning to artificial intelligence?
The terms, machine learning, deep learning and artificial intelligence are closely related, but they are not the same thing. More importantly, machine learning and deep learning are not AI. Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence, while deep learning is a subset of machine learning. Machine learning and deep learning are merely techniques for achieving artificial intelligence, but they are not AI. However, through the use of machine learning and deep learning, we may be able to achieve AI in the future years.
Conclusion
Do you now understand the difference between artificial intelligence (AI), deep learning (DL) and machine learning (ML)? Having read through our article and gone through the various applications highlighted, you should have a clearer understanding of the concepts. I hope our article has been a useful guide to you and increased your level of knowledge. Feel comfortable to add your thoughts on the comments section or ask for clarity on any areas you need more expounding on.


